Digital To Green, Information Technology Is At The Forefront Of Sustainable Tech Revolution
Holding PG Diploma in Finance from Management Development Institute, Nidhi has been associated with Capgemini for over eight years now, prior to which she had worked with corporates such as Cognizant, Dell Services, and Langham Capital.
The COVID pandemic has forced organizations to consider the larger and wider impact they have on the environment. Increasing focus on environment, social and governance(ESG) metrics is driving greater awareness of the carbon footprint of each organization. One function that has historically escaped close scrutiny and evaluation on its carbon footprint is Information Technology(IT).
Enterprise IT across data centers, networks, user devices, and applications is responsible for dramatically significant carbon emissions. For instance, in terms of comparison, it is estimated that the carbon footprint of a major cloud computing solution provider is equivalent to having 64,000 cars on the road for a year. With growing adoption of big data and AI, data centers themselves represented one percent of the world's energy demand in 2019, majority of which are still powered with fossil fuels, denoting the rising environmental foot print of enterprise IT.
In addition, over 50 million tons of e-waste is generated each year, and this figure is rising. Only 15-20 percent of this waste is currently being recycled. Against this backdrop, there is a strong case for designing innovative technology solutions to reduce the environmental footprint of an organization (IT for Sustainability), in addition to reducing the environmental impact of IT itself (Sustainable IT).
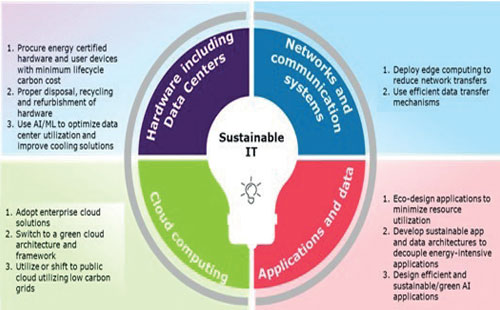
Leveraging IT Sustainability To Drive Energy Efficiency
The potential for ESG initiatives across the end-to-end value chain for large organizations is significant. Emerging digital technologies such as IoT, AI, ML, blockchain, and others, enable real time data driven automated decision making capabilities, which in turn drive energy efficiency, water consumption optimization, waste management and reduced greenhouse gas(GHG)emissions.
Google is a pioneer in tech based sustainability solutions. It has launched interactive air pollution maps that measure and combine real time air pollution information with Google Maps. Google's Project Sunroof promotes renewable energy consumption by determining economic viability of installing solar panels at a specific address using Google geo data.
For CXOs,the short term concerns are the investments involved and data security controls. In the long run, operational efficiency and financial savings out weight investments. Additionally, sustainable measures help in establishing employee and customer attractiveness, leading to a favorable brand image. It is becoming a norm(a legal mandate in some countries) to monitor and publish extensive metrics on sustainability and carbon footprint of organizations in regulatory documents and financial reports.
Reducing The Environmental Footprint
Enterprise IT contributes greatly to energy consumption, carbon emissions and electronic waste creation. Across Enterprise IT, there are multiple levers that can be employed to reduce impact on the environment.
With data at the core of every business, energy consumption of data center operations and subsequent energy requirements for cooling have increased significantly. Google, for instance, has leveraged AI/ML technology to reduce 40 percent energy consumption on cooling mechanism and 15 percent reduction on overall energy consumption in data centers. With this, most Google data centers are approximately 50 percent more energy efficient than others in the market. With tech giants such as Amazon, Microsoft, and Google achieving this level of energy efficiency for their data centers, it builds a clear case for organizations to move their data to cloud.
Adopting the principles of a circular economy is vital for sustainability and reducing business risk and increasing profitability. Apple retrieved 61 million pounds of reusable raw materials from discarded iPhones using cutting edge robotics. For e-waste management in other industries, organizations need to procure energy efficient hardware with a trade in or trade-up option at the end of the asset lifecycle. Another alternative is choosing a trusted and reliable recycling partner to dispose or recycle hardware while meeting regulations (particularly removing data from devices).
Prioritizing Sustainable IT For The Future
During the COVID-19 pandemic, it was IT that led the fast paced digital revolution, enabling remote working and digital collaboration. Consequently, tech giants are expected to demonstrate similar leadership in the Green (IT) revolution too. Globally, they are spearheading this revolution with specific use cases which could inspire other sectors.
Closer home, cleantech startups and new age tech companies in India are driving innovative sustainable IT solutions. Flipkart, with its acquisition of Jeeves and F1, is recycling old devices and has created an independent platform for refurbished devices. Additionally, there are recommerce startups like Budli for IT hardware waste management, specifically recycling and refurbishing electronic devices, thus lengthening the lifecycles of devices.
Another example is an IIT-alumni setup/IIM incubated cleantech company called Skilancer Solar, which provides robotic automation and AI-driven solar panel cleaning solutions without water and manual intervention. There are also building energy management solution startups like Podnet that claim to save up to 40 percent energy with AI and IoT.
Outside these small pockets of innovation, prioritizing sustainable IT in India still needs a significant push. Globally, CXOs have cited implementation challenges as a major reason for not prioritizing Sustainable IT initiatives. Lack of expertise and advisory for identification of correct use cases, implementation costs and impact on business continuity are the biggest challenges perceived by the C-suite.
The Way Ahead
The abrupt and harsh nature of the pandemic had created significant concern initially due to its impact on Sustainable IT. However, the pandemic is now being seen as a humbling experience and an emphatic reminder of the criticality of Sustainability, of which Green IT is a key component. Sustainable IT, led by the tech industry, has the potential to steer the world towards resolving environmental challenges. With a clear strategy and roadmap in place, not only will Enterprise IT's environment footprint become greener, but smart and emerging technologies can be leveraged to drive critical innovations in sustainability as well.
The COVID pandemic has forced organizations to consider the larger and wider impact they have on the environment. Increasing focus on environment, social and governance(ESG) metrics is driving greater awareness of the carbon footprint of each organization. One function that has historically escaped close scrutiny and evaluation on its carbon footprint is Information Technology(IT).
The abrupt and harsh, nature of the pandemic had created significant concern initially due to its impact on Sustainable IT
Enterprise IT across data centers, networks, user devices, and applications is responsible for dramatically significant carbon emissions. For instance, in terms of comparison, it is estimated that the carbon footprint of a major cloud computing solution provider is equivalent to having 64,000 cars on the road for a year. With growing adoption of big data and AI, data centers themselves represented one percent of the world's energy demand in 2019, majority of which are still powered with fossil fuels, denoting the rising environmental foot print of enterprise IT.
In addition, over 50 million tons of e-waste is generated each year, and this figure is rising. Only 15-20 percent of this waste is currently being recycled. Against this backdrop, there is a strong case for designing innovative technology solutions to reduce the environmental footprint of an organization (IT for Sustainability), in addition to reducing the environmental impact of IT itself (Sustainable IT).
Leveraging IT Sustainability To Drive Energy Efficiency
The potential for ESG initiatives across the end-to-end value chain for large organizations is significant. Emerging digital technologies such as IoT, AI, ML, blockchain, and others, enable real time data driven automated decision making capabilities, which in turn drive energy efficiency, water consumption optimization, waste management and reduced greenhouse gas(GHG)emissions.
Google is a pioneer in tech based sustainability solutions. It has launched interactive air pollution maps that measure and combine real time air pollution information with Google Maps. Google's Project Sunroof promotes renewable energy consumption by determining economic viability of installing solar panels at a specific address using Google geo data.
For CXOs,the short term concerns are the investments involved and data security controls. In the long run, operational efficiency and financial savings out weight investments. Additionally, sustainable measures help in establishing employee and customer attractiveness, leading to a favorable brand image. It is becoming a norm(a legal mandate in some countries) to monitor and publish extensive metrics on sustainability and carbon footprint of organizations in regulatory documents and financial reports.
Reducing The Environmental Footprint
Enterprise IT contributes greatly to energy consumption, carbon emissions and electronic waste creation. Across Enterprise IT, there are multiple levers that can be employed to reduce impact on the environment.
With data at the core of every business, energy consumption of data center operations and subsequent energy requirements for cooling have increased significantly. Google, for instance, has leveraged AI/ML technology to reduce 40 percent energy consumption on cooling mechanism and 15 percent reduction on overall energy consumption in data centers. With this, most Google data centers are approximately 50 percent more energy efficient than others in the market. With tech giants such as Amazon, Microsoft, and Google achieving this level of energy efficiency for their data centers, it builds a clear case for organizations to move their data to cloud.
Adopting the principles of a circular economy is vital for sustainability and reducing business risk and increasing profitability. Apple retrieved 61 million pounds of reusable raw materials from discarded iPhones using cutting edge robotics. For e-waste management in other industries, organizations need to procure energy efficient hardware with a trade in or trade-up option at the end of the asset lifecycle. Another alternative is choosing a trusted and reliable recycling partner to dispose or recycle hardware while meeting regulations (particularly removing data from devices).
Prioritizing Sustainable IT For The Future
During the COVID-19 pandemic, it was IT that led the fast paced digital revolution, enabling remote working and digital collaboration. Consequently, tech giants are expected to demonstrate similar leadership in the Green (IT) revolution too. Globally, they are spearheading this revolution with specific use cases which could inspire other sectors.
Closer home, cleantech startups and new age tech companies in India are driving innovative sustainable IT solutions. Flipkart, with its acquisition of Jeeves and F1, is recycling old devices and has created an independent platform for refurbished devices. Additionally, there are recommerce startups like Budli for IT hardware waste management, specifically recycling and refurbishing electronic devices, thus lengthening the lifecycles of devices.
Another example is an IIT-alumni setup/IIM incubated cleantech company called Skilancer Solar, which provides robotic automation and AI-driven solar panel cleaning solutions without water and manual intervention. There are also building energy management solution startups like Podnet that claim to save up to 40 percent energy with AI and IoT.
Outside these small pockets of innovation, prioritizing sustainable IT in India still needs a significant push. Globally, CXOs have cited implementation challenges as a major reason for not prioritizing Sustainable IT initiatives. Lack of expertise and advisory for identification of correct use cases, implementation costs and impact on business continuity are the biggest challenges perceived by the C-suite.
The Way Ahead
The abrupt and harsh nature of the pandemic had created significant concern initially due to its impact on Sustainable IT. However, the pandemic is now being seen as a humbling experience and an emphatic reminder of the criticality of Sustainability, of which Green IT is a key component. Sustainable IT, led by the tech industry, has the potential to steer the world towards resolving environmental challenges. With a clear strategy and roadmap in place, not only will Enterprise IT's environment footprint become greener, but smart and emerging technologies can be leveraged to drive critical innovations in sustainability as well.
